Tiselius and Kabat in 1939 showed that antibodies belong to the γ-globulin fraction of serum proteins
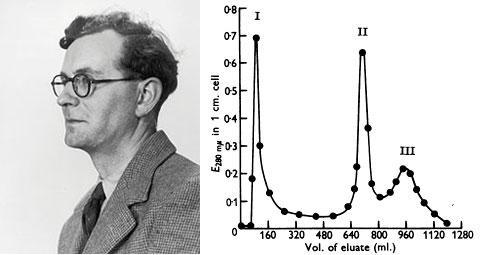
Porter digested γ-globulins with papain, a proteolytic enzyme, and recovered 3 fractions: Fractions I and II of molecular weights between 50 and 55KDa retained the antigen binding capacity, whereas fraction III, of 80 KDa was crystallizable, and had a higher carbohydrate content (Porter RR, Biochem J. 73:119-127, 1959).
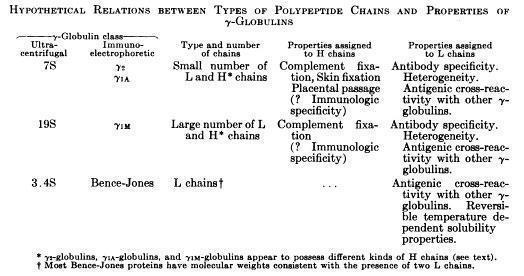
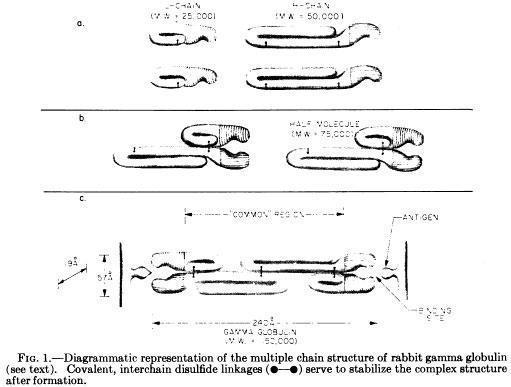
Edelman and Poulik reported that rabbit 7S γ-globulins and human myeloma proteins reduced in strong urea solutions and alkylated, separated into heavy (H) and light (L) chains bound by disulfide bonds (Edelman GM and Poulik MD, J Exp Med. 113:861-884, 1961)
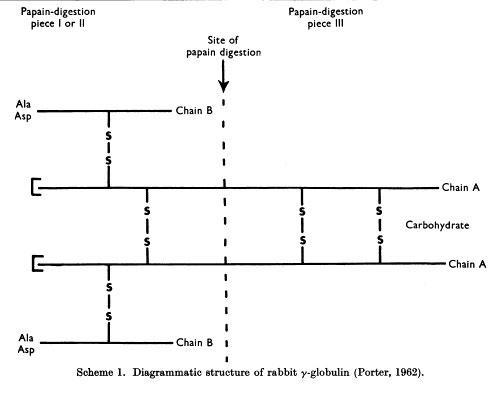
Porter and colleagues proposed the basic Y structure of four polypeptide chains and 5 interchain disulfide bonds (Fleischman JB et al., Biochem J. 88:220-228, 1963)
Dreyer and Bennett proposed that the V and C regions must be the products of different genes (Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 54: 864-869, 1965)
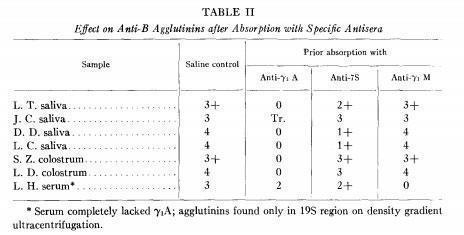
Tomasi and coworkers demonstrated that IgA present in saliva and colostrum is produced locally and secreted as a dimer or trimer by (Tomasi TB et al., J Exp Med 121:101-124, 1965) and Newcomb and coworkers demonstrated the existence of the secretory piece (Newcomb RW et al., J immunol 101:905-913, 1968).
Hood and Ein confirmed that the Lambda chain is encoded by two separate genes that are expressed as a single polypeptide chain (Nature 220:764-767, 1968)
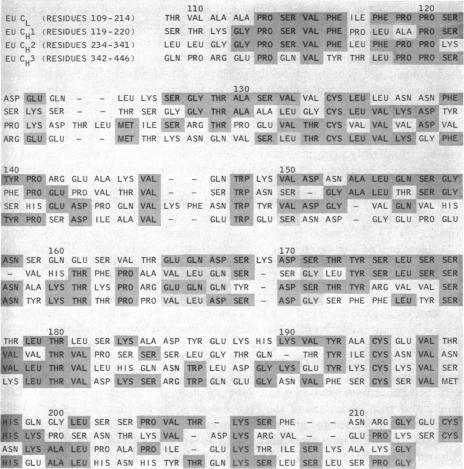
Edelman and coworkers reported the first complete sequence of a γG immunoglobulin molecule and demonstrated the existence of variable (V) and constant (C) regions in the H and L chains (Edelman GM et al., Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 63:78-85, 1969)
Edelman and Porter shared the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1972 “for their discoveries concerning the chemical structure of antibodies”
Gerald M. Edelman – Facts. Nobelprize.org. Nobel Media AB 2014.
Rodney R. Porter – Facts. Nobelprize.org. Nobel Media AB 2014.
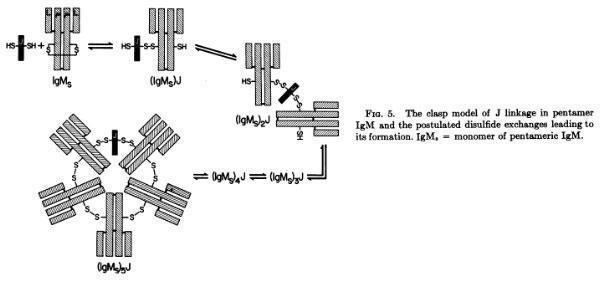
Koshland and coworkers demonstrated that the monomers of the polymeric IgM and IgA are linked by the J chain in a clasp way (Halpern MS and Koshland ME. Nature 228:1276-1278, 1970; Chapuis RM, Koshland ME, Proc Nat Acad Sci 71:657-661, 1974)
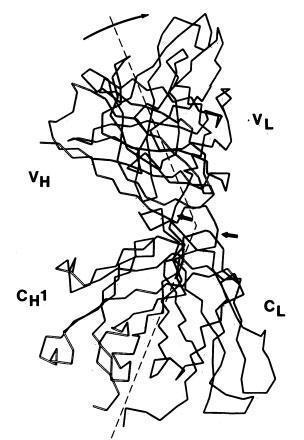
Poljak and colleagues described the three-dimensional structure of IgG(l) myeloma protein (Poljak et al., Proc Nat Acad Sci 71. 3440-3444, 1974).
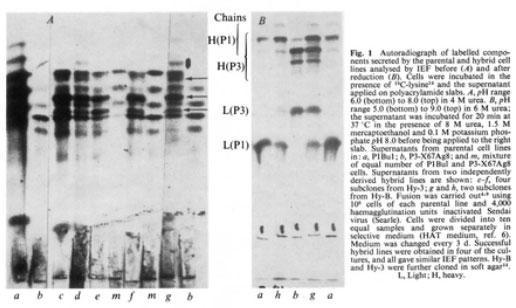
Kohler and Milstein (Nature 256: 495-497, 1975) reported that the fusion of a myeloma cell with a spleen specific antibody-producing cell results in a hybridoma that produces monoclonal antibodies against the specific antigen. Continuous culture of cloned hybrid cells allows the production of large amounts of monoclonal antibodies against the desired antigen.
In the late 1970s, Tonegawa and colleagues in a series of elegant experiments demonstrated that immunoglobulin V and C genes undergo somatic rearrangements to form the complete immunoglobulin gene (Hozumi N, Tonegawa S, Proc Nat Acad Sci 73: 3628- 3632, 1976; Brack C et al., Cell 15:1-14, 1978; Sakano et al., Nature 277:627-633, 1979; Sakano et al., Nature 280: 288-294, 1979; Tonegawa S. Nature 302:575, 1983)
In 1984, Niels Jerne, Georges Kohler and Cesar Milstein were awarded with the Nobel Prize for their discovery of the hybridomas technology for the production of large amounts of monoclonal antibodies for experimental, analytical, diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Niels K. Jerne – Facts. Nobelprize.org. Nobel Media AB 2014.
Georges J.F. Köhler – Facts. Nobelprize.org. Nobel Media AB 2014.
César Milstein – Facts. Nobelprize.org. Nobel Media AB 2014.
In 1987, Susumo Tonegawa was awarded with the Nobel Prize for his discoveries on the mechanisms of somatic rearrangement of the immunoglobulin genes.
Susumo Tonegawa – Facts. Nobelprize.org. Nobel Media AB 2014.
Acknowledgement
History kindly supplied by Dr Luis Garcia – Immunopaedia Steering Committee
Luis F García
Emeritus Professor
Grupo de Inmunología Celular e Inmunogenética
Universidad de Antioquia
Medellín, Colombia
IUIS Education Committee
Immunopaedia Steering Committee