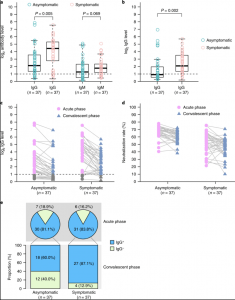
IgG and IgM levels in the acute and convalescent phases in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2. a, The comparison of virus-specific antibody levels in asymptomatic patients (n = 37) and symptomatic patients (n = 37) with acute infections. b, IgG levels in patients with convalescent-phase COVID-19 who were discharged from the hospital. c, Dynamic changes in virus-specific IgG levels in the acute and convalescent phases. d, Dynamic changes in neutralizing serum antibodies in the acute and convalescent phases. Results are expressed as the average of two independent experiments. e, IgG-positive proportions of patients with COVID-19 in the acute and convalescent phases. The box plots in a and b show the medians (middle line) and first and third quartiles (boxes), and the whiskers show 1.5× the IQR above and below the box. Unpaired, two-sided Mann–Whitney U test P values are depicted in the plots, and the significant P value cutoff was set at 0.05. (Source: Long et al., 2020)
A recent publication in Nature Medicine investigated the acute antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Virus-specific IgG and IgM were measured in serum samples from asymptomatic and symptomatic individuals. In the asymptomatic group, 81.1% tested positive for IgG, and 83.8% of the symptomatic group tested positive for IgG approximately 3–4 weeks after exposure. It was noted that IgG levels in the symptomatic group were significantly higher than those in the asymptomatic group in the acute phase. When the authors followed both asymptomatic and symptomatic patients over time, they found that the IgG levels declined after 8 weeks by up to almost 90% in some individuals. The authors conclude: “we observed that IgG levels and neutralizing antibodies in a high proportion of individuals who recovered from SARS-CoV-2 infection start to decrease within 2–3 months after infection.” These results open the question whether there is sustained immunity to SARS-CoV-2 infection, but also how best to interpret serological surveys beyond the acute infection stage and in the convalescent stage.
Journal Article: Long et al., 2020. Clinical and immunological assessment of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections. Nature Medicine
Summary by Clive Gray










