Most antibody treatments used in cancer therapy rely on IgG antibodies, which are effective in blood-borne cancers but have limited success against ovarian cancer. This new approach uses IgE antibodies, typically known for triggering allergic responses or attacking parasites, but now repurposed to enhance immune cell activity in tumour environments.
Unlike IgGs, which primarily circulate in the blood, IgE binds tightly to immune cells in tissues, allowing it to activate tissue-resident immune cells, such as macrophages and T cells, directly at the tumour site.
Researchers have revealed how a novel IgE-based antibody therapy reactivates immune cells in patients with ovarian cancer, showing promise for a new class of cancer immunotherapy (Figure 1). The findings represent the first human-focused evidence of IgE-driven immune activation in a solid tumour setting.
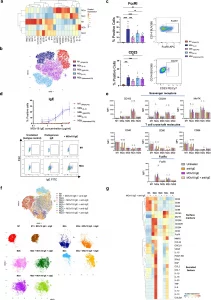
Figure 1: In vitro-derived human macrophage subsets express FcεRs, bind MOv18 IgE and exhibit a net pro-inflammatory phenotypic shift following IgE stimulation. Evaluation of in vitro-derived human macrophage subsets FcεR expression, MOv18 IgE binding and phenotypes following FcεR:IgE cross-linking by polyclonal anti-IgE antibodies. a Heatmap displaying the scaled expression of surface markers (MFI) (flow cytometry) (n = 9 CD86, CD80, CD40, CD206, CD204, CD163, MerTK; n = 8 FcεRI; n = 7 CD23; n = 3 CD200R) and secreted factors (pg/ml) in cell culture supernatants (Luminex) (n = 5). b tSNE plot visualising the in vitro-derived macrophage subsets based on surface marker expression (flow cytometry) (n = 2). c Comparison of FcεRI (n = 9) and CD23 (n = 7) expression, with representative flow cytometry plots for M2a macrophages. d Assessment of MOv18 IgE binding (n = 3), with representative flow cytometry plots for M1 and M2a macrophages. e Comparison of surface marker expression following FcεR:IgE cross-linking (anti-IgE: cross-linking endogenous IgE only; anti-IgE + MOv18 IgE: cross-linking endogenous IgE and exogenously applied MOv18 IgE) (flow cytometry) (n = 9 CD163, CD204, MerTK; n = 6 FcεRI; n = 5 CD40, CD80, CD86). f Composite and faceted tSNE plots visualising the in vitro-derived macrophage subsets based on surface marker expression following FcεR:IgE cross-linking (flow cytometry) (n = 2). g Following detection of IgE-mediated repolarisation of M2a and M2c, the effect of FcεR:IgE cross-linking on the secretome of M2a and M2c, as well as M1, was assessed by Luminex measurement of secreted factors in macrophage culture supernatants. Heatmap displaying the scaled expression of surface markers (MFI) (flow cytometry) (n = 9 CD86, CD80, CD40, CD206, CD204, CD163, MerTK; n = 8 FcεRI; n = 7 CD23; n = 5 CD39; n = 3 CD200R) and secreted factors (pg/ml) in cell culture supernatants (Luminex) (n = 8) following FcεR:IgE cross-linking. Data shown as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was calculated using a repeated measures 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test (c, e); *Padj <0.05, **Padj <0.01, ***Padj <0.001 and ****Padj <0.0001.
The researchers focused on a first-in-class IgE antibody called MOv18, which targets the folate receptor alpha, a protein commonly found on ovarian cancer cells. MOv18 demonstrated an ability to:
- Activate suppressed macrophages in ovarian cancer patient samples
- Kill cancer cells directly via macrophage stimulation
- Reinvigorate T cells, reversing the immune-suppressive environment created by tumours
In both healthy donor-derived and patient-derived macrophages, ovarian cancer fluid was shown to suppress immune responses. However, MOv18 IgE reversed this effect, reprogramming macrophages to fight cancer and helping T cells re-engage with the tumour. Importantly, tumor biopsies from two patients showed an increase in macrophage and T cell infiltration post-treatment — a sign of effective immune activation.
Understanding how IgE uniquely engages the immune system may pave the way for personalised immunotherapies for patients who do not respond to current treatments.
Journal article: Osborn, G., et al., 2025. Hyperinflammatory repolarisation of ovarian cancer patient macrophages by anti-tumour IgE antibody, MOv18, restricts an immunosuppressive macrophage:Treg cell interaction. Nature Communications.
Summary by Stefan Botha










