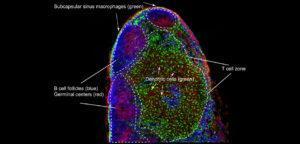
A mouse lymph node section showing B cell follicles (anti-B220, blue) containing germinal centers (peanut agglutinin (PNA), red), in which B cells are selected for high affinity antibody specificity. CD11b+ dendritic cells CX3CR1-GFP, green) are located in the T cell zone, as well as and subcapsular sinus macrophages (CX3CR1-GFP, green) are present above prominent B cell follicles (empty areas).
By Ashley Moseman and Uli von Andrian, Harvard Medical School. (Source: https://www.cell.com/immunity/image-resource-lymphnode)
γδ T cells are well known for their wide range of functional properties that play a role in immunity against pathogens and tumours. γδ T cells have also been shown to participate in induction of humoral immune responses by helping B cells. Whether γδ T cells directly interact with B cells or indirectly affect humoral immunity is not known. Additional studies have shown than γδ T cells promote B cell hypermutation by expressing follicular T helper cells (Tfh)-like properties such as expression of CXCR5 (allowing migration of the B cell follicle), CD40 ligand (crucial for B cell activation) and Il-4 and IL10 cytokine secretion (facilitating IgG class switching). However, it not known whether γδ “Tfh-like” cells truly exist.
Rezende and colleagues, aimed to determine mechanisms by which γδ T cells control and/or contribute to induction of humoral immunity. Rezende et al., used murine models of immunization with complete freund’s adjucant (CFA) or alum, or pristine-induced lupus to study γδ T cell responses. Researchers, observed that immunizing TCRγδ knockout mice resulted in reduced antibody serum levels, as well lower frequencies of Tfh cells that also had low expression of CD40L. This suggests that in the absence of γδ T cells , the Tfh compartment is dysfunctional in providing help to B cells. Additionally, researchers observed that though γδ T cells expressed CXCR5, PD-1 and ICOS, but have limited expression of CD40L and do not express Bcl6 (Tfh transcriptional factor) nor produce IL-21. This suggests that these γδ T cells are not “Tfh-like” cells.
Studies by others have shown that induction of Bcl6 is mediated by upregulation of Ascl2 (transcription factor) via the β-catenin pathway. Induction of Ascl2 viaβ-catenin activation molecules (Wnt agonist) initiates commitment to the Tfh lineage by preventing differentiation into other T helper subsets. Finally, researchers showed that CXCR5+γδ T cells express high transcriptional levels of the Wnt ligands, Wnt8a and Wnt8b, which results in upregulation of CXCR5 in CD4 T cells.
In summary, this study demonstrates how γδ T cells participate in humoral immunity. Briefly, activation γδ T cells by antigens induces expression of CXCR5, which facilitates migration towards the follicle. Where γδ T cells present antigen to CD4 T cells, as well as release Wnt ligands which induce AScl2, initiating Tfh programming, with assistance from dendritic cells. These induced Tfh cells then interact with B cells and provide signal necessary for differentiation.
Journal Article: Rezende et al., 2018. γδ T cells control humoral immune response by inducing T follicular helper cell differentiation. Nature Communication
Article by Cheleka AM Mpande










