A recent phase 2 study suggests that a new drug called enoblituzumab, a monoclonal antibody, is safe for men with aggressive prostate cancer and may have a positive effect on cancer throughout the body (Figure 1). If further studies confirm these results, enoblituzumab could be the first promising immunotherapy agent based on antibodies to effectively treat prostate cancer.
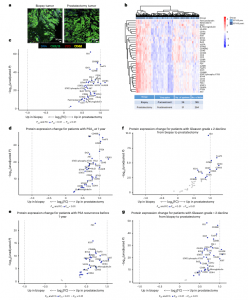
Figure 1: Digital spatial profiling of the TME in pretreatment biopsies and posttreatment prostatectomies stratified by clinical outcomes. a, Immunofluorescent staining of pretreatment (biopsy) and posttreatment (radical prostatectomy) tissue to select ROIs for DSP. Matched-patient pretreatment biopsies (n = 28 patients and 199 tumor regions) and posttreatment prostatectomies (n = 31 patients and 264 tumor regions) were evaluated. Tumor cells were identified with CK8/18, CD3 for T cells, CD68 for myeloid cells and Cyto83 for DNA content analysis. Two illustrative ROIs are depicted. b, Heatmap showing the relative quantification of 34 proteins
detected in tumor ROIs in biopsy (pretreatment) and radical prostatectomy (posttreatment) specimens. c, Volcano plot overview of fold-changes (FC) in protein expression in tumor ROIs between pretreatment biopsy and posttreatment prostatectomy. d–g, Volcano plot overview of tumor region protein expression change for patients with PSA 0 at 1 year after prostatectomy (d) or PSA recurrence prior to 1 year (e), and protein expression change for patients who had Gleason-grade group downgrade ≥−2 from biopsy to prostatectomy (f) or <−2 (g). Proteins that remain significant after the Benjamini–Hochberg adjustment (Padj < 0.01) are blue.
During the clinical trial, 32 men with high-risk or very high-risk prostate cancers, who were scheduled for prostate cancer surgery, received six weekly infusions of enoblituzumab before the surgery. They were then monitored for an average of 30 months after the surgery. After 12 months, 66% had undetectable levels of prostate-specific antigen, indicating no remaining signs of the disease, with the drug was generally well-tolerated.
Enoblituzumab works by attaching to a protein called B7-H3, which is found in abundance on prostate cancer cells and is believed to hinder the immune system’s ability to attack these cells. The new drug has a two-fold effect on cancer: it blocks B7-H3’s inhibitory effect on the immune system’s recognition and elimination of cancer cells, and it triggers a process known as antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). ADCC leads to the destruction of tumor cells by activating other immune cells like macrophages and natural killer cells.
It is important to note that while these findings are exciting, they are preliminary and need to be confirmed through larger studies involving more participants. If enoblituzumab continues to show positive results in larger randomized studies, it could open up a new pathway for immunotherapy in treating various types of cancer.
Journal article: Shenderov, E., et al., 2023. Neoadjuvant enoblituzumab in localized prostate cancer: a single-arm, phase 2 trial. Nature Medicine.
Summary by Stefan Botha