Interleukin (IL)-31 is a neuroimmune cytokine which is involved in the pathophysiology of atopic dermatitis through the maintainnance of an inflammatory state and pruritus (Figure 1).
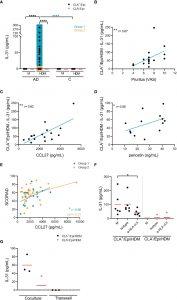
Figure 1: HDM-induced IL-31 by memory T cells correlates with patient’s pruritus and plasma CCL27 and periostin, partially depends on HLA class II molecules and the cell-cell contact with epidermal cells, and is restricted to CLA+ T-cells subset. (A) IL-31 (pg/mL) produced by CLA+/- T-cell cocultures in basal conditions (M) or stimulated with HDM in AD-(n=58) and C-(n=11) derived samples. Correlations of CLA+/Epi/HDM IL-31 production in group 1 with (B) pruritus (n=17), and plasma (C) CCL27 (n=17) and (D) periostin (n=13) levels. (E) Correlation between plasma CCL27 levels and SCORAD in group 1 (n=15) and group 2 (n=31) of patients. (F) HDM-activated CLA+/- T-cell cocultures were treated with HLA class II neutralizing antibody or control IgG isotype at day 0, and IL-31 production (pg/mL) at day 5 was compared with respect to isotype values (n=6). Red bar indicates the mean. (G) CLA+/- T cells were added in the upper chamber and HDM-stimulated epidermal cells suspension in the lower chamber of the 96-well transwell plate and IL-31 (pg/mL) was measured at day 5. Data for three representative patients. AD, atopic dermatitis; C, control subjects; CLA, cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen T cells; Epi, epidermal cells suspension; HDM, house dust mite; M, untreated; SCORAD, scoring atopic dermatitis. ns: p >.05; *p <.05; **p <.01; ****p <.0001.
Lidia Sans-de San Nicolàs, et al., studied IL-31 production by memory cells following cell culture, cytokine quantification and gene analysis. The authors investigated IL-31 production by memory T cells cultured with autologous lesional epidermal atopic dermatitis cells under HDM stimulation. Two groups were defined – group 1, where IL-31 was produced by CLA+ cells and group 2, without IL-31 production. A higher inflammatory phenotype was observed in group 1 when compared to group 2.
In group 1, a correlation was found between IL-31 production and HDM specific IgE and total IgE. Furthermore IL-31 production by memory T cells was found to be associated with higher levels of IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, IL-22, IL-17A with equal expression to IL-13. Between the two groups of patients, an increased level of IgE specific to HDM was found in group 1.
To further characterize group 1 and 2, the authors evaluated changes in lesional skin tissue from patients using gene array analysis finding that in group 1, IL-17 and IL-21 mRNA expression was higher. Finally, high levels of IgE was observed in patients with IL-31 production by memory T cells, specific to the CLA+ subset.
From these results, the authors could hypothesise about an correlation between IL-31, periostin and CCL27 which act like a chemokine to CLA+ T cells. In addition, they described limited production of IL-31 by T cells to CLA+ cells subset which reflect specific mechanisms taking place in A.D and others cutaneous diseases.
Journal article: Sans-de San Nicolàs, L., et al., 2023. Allergen sensitization stratifies IL-31 production by memory T cells in atopic dermatitis patients. Frontiers in Immunology.
Summary by Frederic Christian Diaz










