A new study has identified the amino acid asparagine as a critical regulator of germinal center (GC) B cells, which are essential for producing high-quality antibodies. The findings highlight the pivotal role of asparagine metabolism in maintaining B cell homeostasis and immune response, with implications for tackling diseases involving abnormal B cell activity.
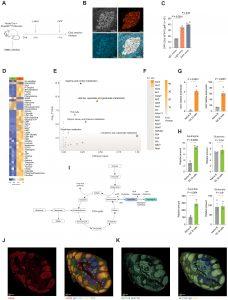
Figure 1: GC B cells have highly active protein synthesis and asparagine metabolism. (A) Schematic of in vivo BONCAT in Aicda-Cre Rosa26STOPtdTomato GC-reporter mice. h, hours. (B) Representative immunofluorescence images of splenic GCs labeled with OPP, tdTomato (activation-induced cytidine deaminase, AID), and l-AHA. Scale bars, 50 μm. (C) Quantification of OPP (20 μM) incorporation ex vivo (30 min) in naïve, LZ GC, and DZ GC B cells from non-reporter WT mice (n = 4). (D) Heatmap of significantly differentially abundant metabolites (Padj < 0.05) measured by LC-MS (N = 3 pools of three mice per pool). (E) Integrated pathway analysis of differentially abundant metabolites from (D) and expressed genes from ImmGen in GC compared with that in naïve B cells (GSE15907). (F) Heatmap of relative gene expression of KEGG AAG pathway in GC versus naïve B cells, represented as fold change. Data are from GSE133971 (26). (G) Relative expression of Asns and Got2 in GC and naïve B cells at day 7 after SRBC immunization, normalized to Ubiquitin C (Ubc) (n = 4 mice). (H) Relative amounts of asparagine, aspartate, glutamine, and glutamate measured by LC-MS (N = 3 pools of three mice) as in (D). (I) Diagram of asparagine synthesis and its association with the TCA cycle. (J) Multiplexed CellDIVE images of a normal human tonsil section, with immunofluorescence staining for ASNS, CD21, IgD, MZB1, and CD3. Representative of three separate tonsils. Scale bars, 250 μm. (K) Multiplexed CellDIVE images of normal human tonsil serial section of (J), with immunofluorescence staining for SLC1A5 (ASCT2), CD21, and IgD. Representative of three separate tonsils. Scale bars, 250 μm. Statistical significance was determined by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s multiple testing correction (C), two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple testing correction (D), hypergeometric test (E), and unpaired two-tailed t test [(G) and (H)]. Data representative of two independent experiments [(B) to (D), (G), and (H)]. Data are presented as the means ± SEM.
The researchers discovered that asparagine is vital for sustaining the metabolic activity of GC B cells. When asparagine was depleted—either through dietary restriction or the administration of the drug Asparaginase—GC B cell function was significantly impaired. This deprivation resulted in reduced mitochondrial activity and diminished production of essential building blocks, such as nucleotides, which are critical for cell proliferation and antibody generation. The loss of asparagine also weakened the ability of GC B cells to produce high-quality antibodies during a flu infection, particularly in cells with an already compromised capacity to synthesize asparagine.
The findings highlight the importance of asparagine metabolism in immune regulation and reveal a potential vulnerability in GC B cells that could be therapeutically targeted. Abnormal B cell responses are central to many autoimmune diseases and malignancies. By targeting asparagine metabolism, it may be possible to modulate B cell function to treat these conditions.
These findings not only enhance our understanding of the metabolic requirements of B cells but also highlight the potential of metabolic interventions to influence immune responses in a range of diseases. This research represents a significant step forward in linking metabolism to immune regulation, paving the way for innovative therapeutic strategies.
Journal article: Yazicioglu., Y.F., et al, 2024. Asparagine availability controls germinal center B cell homeostasis, Science Immunology.
Summary by Stefan Botha










