Using natural compounds to fight disease is not something new. Using novel screening methods, it is possible to isolate useful compounds that have the potential to be used as therapeutics. Three natural compounds have been found that may have potential in fighting coronaviruses. In a new study, researchers have screened a large library of natural substances using X-ray and found that they bound to an enzyme which is essential for replication of the coronavirus (Figure 1). Importantly, these compounds are already being used in drugs today however targeting coronavirus directly still remains an important goal.
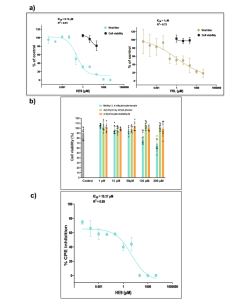
Figure 1: Effect of the natural compounds on SARS-CoV-2 loading in Vero cells. a The viral titer and cell viability were quantified by qRT-PCR (●) and CellTiter-Glo luminescence method (■), respectively. IC50- and R-squared values for viral titers are shown. IC50-values were calculated by fitting the data to the sigmoidal function as previously described4. Compounds concentrations are presented in log scale for interpolation. HE9 was diluted to a stock concentration of 100 mM in DMSO, while YRL was diluted in sterile water to a 50 mM stock concentration. All compounds were stored at −20 °C. Individual data points represent means ± SD from four independent replicates in two biological experiments. Values were plotted in a line graph with error bars displaying standard deviation. b Cell viability in the presence of the three compounds was determined by CellTiter-Glo luminescence method. Individual data points from three independent replicates in three biological experiments. c CPE inhibition was determined by CellTiter-Glo luminescence method. IC50- and R-squared values are shown. IC50-values were calculated by fitting the data to the sigmoidal function. Individual data points represent means ± SD from three independent replicates in one biological experiment. Values were plotted in a line graph with error bars displaying standard deviation.
The researchers tested 500 substances from the Karachi Library of Natural Compounds if they bind to the papain-like protease of the novel coronavirus, whereby the papain-like protease (PLpro) is crucial for viral replication and it also blocks an important immune system protein, ISG15 which is important for the cells defence.
From the screening the researchers were able to identify three phenols that bind the enzyme, i.e; hydroxyethylphenol (YRL), (from Lawsonia alba), which can be found in virgin olive oil and wine; Hydroxybenzaldehyde (HBA) an anti-tumor agent from Acalypha torta and Methyldihydroxybenzoate (HE9) from Tagetes patula, which servese as an anti-oxidant with anti-inflammatory effects.
This study is important in highlighting natural compounds for drug development.
Journal article: Srinivasan, V, et al., 2022. Antiviral activity of natural phenolic compounds in complex at an allosteric site of SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease. Communications Biology.
Summary by Stefan Botha










