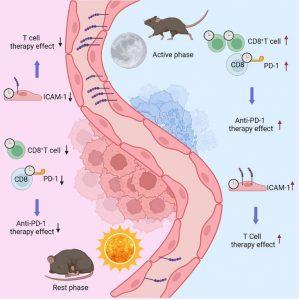
In a recent study, researchers investigated the circadian regulation of CD8+ T cells and its implications for cancer immunotherapy efficacy (Figure 1). It highlights that both the quantity and quality of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), particularly CD8+ T cells, exhibit circadian oscillations. These oscillations are driven by the intrinsic circadian clocks of the leukocytes and the rhythmic expression of adhesion molecules on endothelial cells, which facilitate leukocyte infiltration.
The research utilized murine models and human cancer samples to demonstrate the time-of-day-dependent variations in TILs. The findings suggest that the efficacy of immunotherapy, including CAR T cell therapy and immune checkpoint blockade, could be significantly influenced by the timing of treatment administration. Specifically, administering these therapies at times when CD8+ T cell infiltration and function are at their peak may enhance their effectiveness.
Key Takeaways
- Circadian Regulation of CD8+ T Cells:
- CD8+ T cells have intrinsic circadian clocks that regulate their infiltration into tumors and their antitumor activities.
- These circadian rhythms affect the expression of key molecules involved in T cell trafficking and adhesion, such as ICAM-1.
- Impact on Immunotherapy:
- The timing of immunotherapy administration can influence treatment outcomes due to the circadian variation in TIL infiltration and function.
- Optimizing the timing of treatments like CAR T cell therapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors could enhance their efficacy.
- Murine and Human Cancer Models:
- The study’s findings were consistent across both murine models and human cancer samples, underscoring the relevance of circadian rhythms in clinical settings.
- Clinical Implications:
- The research suggests the potential for chronotherapy in cancer treatment, where therapies are timed to align with the body’s biological rhythms to maximize effectiveness.
- Further clinical studies are needed to determine the optimal timing for different types of immunotherapy based on circadian rhythms.
- Future Directions:
- Investigating other immune cell types and their circadian regulation in the tumor microenvironment.
- Exploring the molecular mechanisms underlying circadian control of immune cell functions.
- Developing guidelines for the timing of immunotherapy administration to improve patient outcomes.
Conclusion
This study provides crucial insights into the circadian regulation of CD8+ T cells and its impact on cancer immunotherapy efficacy. By understanding the temporal dynamics of immune cell function, clinicians can potentially enhance the success of immunotherapy treatments through chronotherapy. Further research in this area could lead to more personalized and effective cancer treatment strategies.
Journal article: Wang, C, et al. 2024. Circadian tumor infiltration and function of CD8+ T cells dictate immunotherapy efficacy. Cell.
Summary by Gaurang Telang