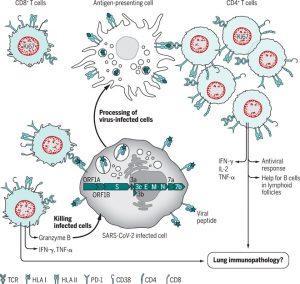
Hypothetical interactions between SARS-CoV-2 infected cells, antigen-presenting cells, CD4 and CD8 T cells. Viral peptides (shown in dark green) will be processed from all parts of the SARS-CoV-2 proteome and presented to the TCR repertoire in the grooves of HLA I molecules on the infected cell, and by HLA II molecules of antigen-presenting cells that have taken up debris from infected cells. SARS-CoV-2-reactive CD4 cells appear to be largely Th1-like, secreting IFN-γ, TNF-α and IL-2. CD8 cells can secrete a similar cytokine profile but also lyse infected target cells. We are unaware of data at present clearly indicating a role of CD4 or CD8 T cells in lung immunopathology, but illustrate here the hypothetical likelihood of this. (Source: Altman & Boyton 2020)
There are a number of studies emerging that show people infected with SARS-CoV-2 make robust T cell responses that target the spike protein, membrane antigens and nucleocapsid, with immunodominant responses against spike (See table below). With recent findings that neutralising antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 wane rapidly after peak symptoms, is there evidence that T cell memory responses linger for longer? A recent perspective article in Science poses this question and provides evidence about the type and duration of T cell responses. An intriguing question is whether the asymptomatic nature of infection in children is possibly due to cross-reactive T cell responses from other Coronaviruses in circulation. There are currently no answers to any of these questions and represents a fertile ground for research. It will also be important to assess whether pending vaccine-induced responses are antibody-mediated or due to the elicitation of a T cell response. In other words, would vaccine-induced T cell immunity represent a mechanism of protection and antibodies a correlate of protection?
Also Read: Rapid decay of IgG to SARS-CoV-2 in people with mild COVID-19
Journal Article: Altman & Boyton. 2020. SARS-CoV-2 T cell immunity: Specificity, function, durability, and role in protection. Science Immunology
Summary by Clive Gray