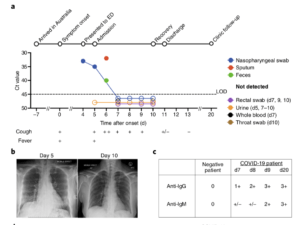
a, Timeline of COVID-19, showing detection of SARS-CoV-2 in sputum, nasopharyngeal aspirates and feces but not urine, rectal swab or whole blood. SARS-CoV-2 was quantified by rRT-PCR; cycle threshold (Ct) is shown. A higher Ct value means lower viral load. Dashed horizontal line indicates limit
of detection (LOD) threshold (Ct = 45). Open circles, undetectable SARS-CoV-2. b, Anteroposterior chest radiographs on days 5 and 10 following symptom onset, showing radiological improvement
from hospital admission to discharge. c, Immunofluorescence antibody staining, repeated twice in duplicate, for detection of IgG and IgM bound to SARS-CoV-2-infected Vero cells, assessed with
plasma (diluted 1:20) obtained at days 7–9 and 20 following symptom onset. (Source: Thevarajan et al., 2020. Breadth of concomitant immune responses prior to patient recovery: a case report of non-severe COVID-19. Nature Medicine.)
As of 23 March 2020, SARS-CoV2 is responsible for almost 350,000 cases and over 15000 deaths globally. We report findings of an Australian COVID-19 Case study of a 47 year woman*.
Thevarajan et al., aimed to determine the “kinetics and breadth of immune responses associated with clinical resolution of COVID-19.” Specifically, the conducted immune-profiling of blood samples at day 7-9 post symptoms, and day 20 (recovered). They observed “Increased antibody-secreting cells (ASCs), follicular helper T cells (TFH cells) and SARS-CoV-2-specific IgM and IgG in blood before symptomatic recovery”. Mild-COVID-19 was also associated with peak CD4 and CD8 T cells (HLA-DR+CD38+) activation, which decreased by day 20. Further researchers showed that COVID-19 was associated with decreased levels of CD16+CD14+ monocytes compared to controls. Lower proportions of these cells could be related to immunopathology and recruitment of cells to the site of infection. Researchers detected lower levels of CD16+CD14+ monocytes in the COVID-19 patient compared to controls. This observation could be related to immunopathology and recruitment to the site of infection. Further, quantification of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines provided no evidence of cytokine storm in this patient.
Findings reported by Thevarajan et al., demonstrate induction of robust multi-factorial immune responses, including adaptive immunity during early stages of SARS-CoV-2 infection. However, more studies are required to determine if similar immune-profiles are detected in other mild/moderate cases and if they are associated with better clinical outcomes.
Thevarajan et al., 2020. Breadth of concomitant immune responses prior to patient recovery: a case report of non-severe COVID-19. Nature Medicine.
*History: Woman presented to emergency department (ED) 11 days after travelling from Wuhan, China to Australia. She exhibited symptoms: lethargy, sore throat, dry cough, pleuritic chest pain, mild dyspnea and subjective fevers which started 4 days before presenting to the ED. Upon detection of SAR-CoV2 in patients nasopharyngeal swabs, patient was admitted. SARS-Cov2 remained detected 5-6 days post symptoms, but was undetectable in urine, whole, nasopharyngeal and rectal swabs from day 7 till discharge (Day 11 ). By Day 13 her symptoms had resolved and remained well at day 20.
Article by Cheleka Mpande











