In the expanding field of immunology, new discoveries about the role of different cells in the manifestation of the immune response is added annually. Neutrophils which were regarded a homogenous population with no immune modulatory functions have been found by researchers to be a novel target for new therapeutics drugs.
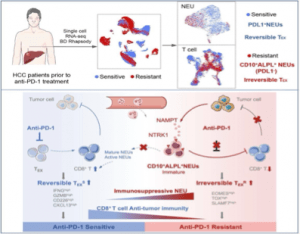
Recently researchers have found out by studying hepatocellular carcinoma patients sample a neutrophils population which is characterized by CD10+ALPL+ Neu, are resistant to anti-PD-1 treatment (Figure 1). These neutrophils were isolated and co-cultured with CD3+ T-cells, showed a decreased in percentage of CD8+ T-cell secreted granzyme B and enhanced the fraction of exhausted CD8+T-cells.
Researchers studied rats after anti-PD-1 therapy, rats infected with CD10-ALPL- Neu did not develop tumors as severe as developed in rats injected with CD10+ALPL+Neus.
The hepatoma cell derived tumor microenvironment secreted NAMPT reprogrammed CD10+ALPL+ Neu through NTRK1 activation promote development of CD10+ALPL+ Neutrophils.
Journal article: Meng, Y., et.al. 2023. Immunosuppressive CD10+ALPL+ neutrophils promote resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy in HCC by mediating irreversible exhaustion of T cells. Journal of hepatology.
Summary by Shubham Kumar