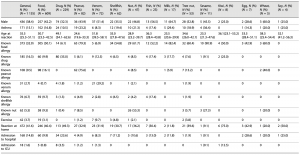
A new study offers important findings on severe allergic reactions, shedding light on the connection between alcohol and nut allergies while revealing patterns that could improve emergency care for all anaphylactic allergies (Table 1). The study highlights the heightened risks for individuals with tree nut allergies and provides insights into broader triggers and symptoms of anaphylaxis—a potentially fatal allergic reaction if untreated.
The research found that consuming alcohol can worsen allergic reactions in individuals with nut allergies, potentially amplifying symptoms to more severe levels. It also raises concerns about nut-flavoured alcoholic beverages, even those made with artificial flavouring, which may contain trace amounts of allergens that could trigger reactions. These findings emphasize the need for heightened caution, particularly during occasions when nut-based treats and specialty beverages are prevalent.
For individuals with nut allergies, the combination of alcohol and allergens may represent a critical risk factor, making awareness and avoidance essential for safety. The study’s findings also call for greater scrutiny of food and beverage labelling practices to ensure clear allergen information is available to consumers.
Anaphylaxis is often triggered by food, insect bites, or medications, and its symptoms can vary widely. While epinephrine is the standard treatment, delays in diagnosis and administration can occur due to gaps in understanding how specific triggers lead to symptoms. The study shows the importance of recognising these patterns for timely and life-saving intervention.
The findings have significant implications for both healthcare providers and individuals with allergies. For medical professionals, identifying patterns between triggers and symptoms can streamline diagnosis and treatment during emergencies, potentially saving lives. For patients, understanding how factors like alcohol consumption or certain foods exacerbate reactions can guide safer choices. The study also highlights the need for improved allergen labelling in the food and beverage industry, particularly for products like nut-flavoured alcoholic drinks that may inadvertently expose consumers to allergens.
Journal article: Roy Khalaf, R., et al, 2024. Symptomatology and Management of Adult Anaphylaxis according to Trigger: A Cross-Sectional Study, International Archives of Allergy and Immunology.
Summary by Stefan Botha