In a recent study, scientists created a biodegradable polymer system that works with the strength of the human immune system to treat the autoimmune and inflammatory illness rheumatoid arthritis (Figure 1). The study draws on prior work using all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), a substance generated naturally by the body that aids in cell growth and development, as well as growing clinical interest in immune system modulation as a means of treating cancer and autoimmune diseases.
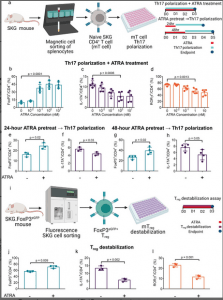
Figure 1: All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) differentially promotes Treg enhancement and Th17 suppression in a concentration dependent manner. a) Experimental schematic and timeline for assessing the effect of ATRA on Th17 and Treg differentiation from naïve CD4+ SKG T (mT) cells. b–d) Quantification of b) FoxP3, c) IL-17A, and d) RORγt expression in CD4+ mT cells differentiated in Th17 inducing conditions with ATRA added at the depicted concentrations. e–h) Quantification of FoxP3 and IL-17A expression in CD4+ T cells pretreated with or without 1 × 10−9 m ATRA for either e,f) 24 or g,h) 48 h prior to Th17 induction for an additional 72 h. i) Experimental schematic for assessing SKG Treg (mTreg) destabilization. j–l) Quantification of j) FoxP3 expression, k) IL-17A expression, and l) RORγt expression in Treg following an IL-6 mediated destabilization assay with or without 1 × 10−9 m ATRA. Data in (b)–(h) and (j)–(l) are the means ± SD of technical replicates from representative experiments; Data in (b)–(d), (j)–(l), and (e)–(h) are representative of three experimental replicates. Statistical analyses in (b)–(d) were performed using one-way ANOVA with post hoc Dunnett’s test; statistical analyses in (e)–(h) and (j)–(l) were performed using unpaired Student’s two tailed t-tests. Schematics in (a) and (i) were composed using BioRender.
The FDA has currently authorised the small chemical ATRA for the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukaemia (APML). It may also be effective in treating autoimmune arthritis and reducing inflammation, according to 20 years of research. ATRA can be injected directly into joints when it is encapsulated using biodegradable polymers, but when it diffuses out of the joint, it enters circulation at much lower amounts, minimising or avoiding adverse effects. It’s interesting to note that ATRA changes disease-causing cells into regulatory T cells, which can treat or halt the illness in other parts of the body.
Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic medications (DMARDs) are often used to treat rheumatoid arthritis patients, and for many of them, this method is effective. Front-line DMARDs have several substantial drawbacks and only properly treat roughly one-third of patients. Immunosuppressive medications can be beneficial for certain people for a while before losing their potency. This may occur if new disease pathways or antibodies that neutralise the drugs develop in the patients’ bodies.
The effort entailed meticulously following the cells from their injection sites to other regions where they circulated and shown efficacy in battling disease, as well as several disease models, each created to illustrate a particular feature of the team’s idea.
Journal article: David A. McBride, D.A., et al., 2023. Immunomodulatory Microparticles Epigenetically Modulate T Cells and Systemically Ameliorate Autoimmune Arthritis. Advanced Science.
Summary by Stefan Botha










