T cell activation markers (TAMs) such as CD27, CD38 and HLA-DR, identified in whole blood or PBMCs, have been shown to differentiate individuals with active TB from those that are latently infected (Acharya et al., 2021; Portevin et al., 2014). These findings led Hiza and colleagues to test the diagnostic capability of a simplified TAM-based assay that takes real-time measurements from a millimetre of blood (Fig 1).
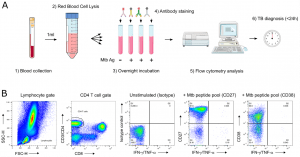
Figure 1: (A) “TAM-based assay procedure overview from blood collection to delivery of results within 24 h. Briefly, a single millilitre of fresh blood was subjected to red blood cell lysis (steps 1 & 2) and white blood cells evenly split between 4 tubes before overnight stimulation (step 3). The following morning, cells were fixed and stained with fluorescent antibodies as detailed in the methods section (step 4). Samples were immediately acquired on a FACSCalibur delivering final results within 24 h following phlebotomy (steps 5 & 6). (B) Representative gating strategy of the TAM-based assay adapted for a 2-laser flow cytometer FACSCalibur apparatus.”
The authors also sought to compare the performance of both CD27 and CD38, as information present suggests that CD38 could perform better (Adekambi et al., 2015; Ahmed et al., 2019). The CD38-based TAM assay performed better than CD27 in distinguishing active TB from non-TB cases, however CD38 had decreased specificity for presumptive TB cases with recent exposure (Hiza et al., 2021).
No differences in diagnostic accuracy were noted when performance of the CD38-TAM assay was compared between HIV positive and negative individuals. This led the authors to the same conclusions as Wilkinson et al (Wilkinson et al., 2016); about TAMs being able to differentiate active from latent TB irrespective of HIV status.
The CD38-TAM assay achieved a specificity 93.4% and sensitivity of 82.2% therefore going beyond the minimum sensitivity (80%) and almost approaching the minimal specificity (98%) highlighted in the WHO target product profile for non-sputum based diagnostic tests (World Health Organization, 2014) (Fig 2).
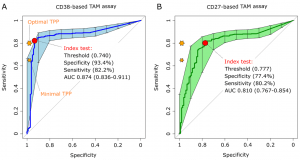
Figure 2: “Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of CD38-based (left plot) and CD27-based index test. The orange stars indicate the target product profile (TPP) minimal (80/98) and optimal (65/98) sensitivity/ specificity values defined by WHO for non-sputum confirmatory TB diagnostic tests. The red circles indicate the index test performance and threshold values yielding the best specificity for a test sensitivity above 80%, the minimal TPP requirement. AUC, area under the curve and 95% confidence intervals within brackets.”
Journal article: Hiza, H., et al., 2021. Case–control diagnostic accuracy study of a non-sputum CD38-based TAM-TB test from a single milliliter of blood. Scientific Reports.
Summary by Vanessa Muwanga
References
Acharya, M.P., Pradeep, S.P., Murthy, V.S., Chikkannaiah, P., Kambar, V., Narayanashetty, S., Burugina Nagaraja, S., Gangadhar, N., Yoganand, R., Satchidanandam, V., 2021. CD38+CD27–TNF-α + on Mtb-specific CD4+ T Cells Is a Robust Biomarker for Tuberculosis Diagnosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 73, 793–801. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab144
Portevin, D., Moukambi, F., Clowes, P., Bauer, A., Chachage, M., Ntinginya, N.E., Mfinanga, E., Said, K., Haraka, F., Rachow, A., Saathoff, E., Mpina, M., Jugheli, L., Lwilla, F., Marais, B.J., Hoelscher, M., Daubenberger, C., Reither, K., Geldmacher, C., 2014. Assessment of the novel T-cell activation marker–tuberculosis assay for diagnosis of active tuberculosis in children: a prospective proof-of-concept study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 14, 931–938. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70884-9
Wilkinson, K.A., Oni, T., Gideon, H.P., Goliath, R., Wilkinson, R.J., Riou, C., 2016. Activation Profile of Mycobacterium tuberculosis–Specific CD4+ T Cells Reflects Disease Activity Irrespective of HIV Status. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 193, 1307–1310. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201601-0116LE
World Health Organization, 2014. High priority target product profiles for new tuberculosis diagnostics: report of a consensus meeting, 28-29 April 2014, Geneva, Switzerland. World Health Organization, Geneva.










