The SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant has been known to cause a less severe disease than the Delta variant despite its improved ability to evade the immune response and induced immune protection by vaccinations and previous infections. The reason why has eluded scientists until now.
A new study by Bojkova, et al., reported on the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant and why it is less efficient than the Delta variant at inhibiting/blocking the host cellular defense mechanism against viruses. This defense mechanism of interest is the “interferon response.” In addition, they have reported that several COVID-19 drugs and drug candidates are effective against the Omicron variant.
The present study on the Omicron variant has described that the variant is more sensitive to inhibition by the so-called interferon response (Figure 1). This may provide an explanation as to why this variant is less severe than previous variants. The researchers also highlighted using cell culture that the Omicron variant remained to be sensitive to eight of the most important antiviral drugs and drug candidates for the treatment of COVID-19 (Figure 1). This included EIDD-1931 (active metabolite of molnupiravir), ribavirin, remdesivir, favipravir, PF-07321332 (nirmatrelvir, active ingredient of paxlovid), nafamostat, camostat, and aprotinin.
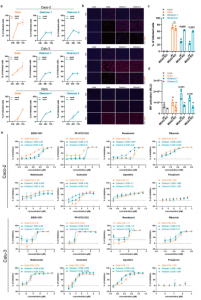
Figure 1: a Caco-2 and Calu-3 cells were infected with SARS-CoV-2 variant Delta (GenBank ID: MZ315141), Omicron 1 (GenBank ID: OL800702) and Omicron 2 (GenBank ID: OL800703) at an MOI of 0.01. The number of infected cells at different time points post infection was determined by immunofluorescence staining of the SARS-CoV-2 S protein. Graphs represent means ± SD of 12 biological replicates. b Representative immunofluorescence images of a are shown (4× magnification). c Virus infection rates in A549-ACE2/TMPRSS2 MDA5-WT (wt) and A549-ACE2/TMPRSS2 MDA5 KO (MDA5 KO) cells 72 h post infection as determined by immunofluorescence staining of the S protein. Graph represents data of four biological replicates. d Induction of IRF transcriptional activity 24 h post infection in a promotor reporter assay. Graph displays means ± SD of four biological replicates. e Dose-dependent effects of selected antiviral compounds on SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and Delta variant isolates. Compounds were added to confluent monolayers and cells were subsequently infected with viral variants at MOI of 0.01. The inhibition rate was evaluated 24 h (Caco-2) and 48 h (Calu-3) post infection by staining of the S protein. Graphs depict means ± SD of three biological replicates. P-values were calculated using two-way ANOVA (c, d). ns, not significant (Bojkova, et al., 2022).
This study is the first to describe, why Omicron infections are less likely to cause severe disease. This study also presented some promising data for the future.
Journal article: Bojkova, D., et al., 2022. Reduced interferon antagonism but similar drug sensitivity in Omicron variant compared to Delta variant SARS-CoV-2 isolates. Cell Research.
Summary by Stefan Botha










