- Patient Presentation
- History
- Differential Diagnosis
- Examination
- Investigations
- Discussion
- Treatment
- Final Outcome
- References
- Evaluation – Questions & answers
- MCQ
Patient Presentation
A 25 year old female presented to her primary healthcare physician complaining of swollen hands for the last week. She had also noticed that over the last two days she was getting swelling around her eyes and was short of breath.
History
History revealed that three weeks ago she had infected skin lesions on her thighs that had been treated with an antibiotic ointment from her doctor.
Past medical history
- No past medical history of note.
- Recent HIV test was negative (2 months ago) with no history of unprotected sex since that time.
Past surgical history
- No past surgical history.
Family History
- Mother has hypertension and is on treatment
- Father has no known medical concerns.
- Four siblings, all healthy
Allergies
- Non known
Medication
- Multivitamins
Travel History
- None noted
Social history
- Not married, 1 child
- Non smoker
- No alcohol consumption
- No illicit drug use
Differential Diagnosis
- Acute renal failure
- Congestive heart failure
- Immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephritis
- Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN)
- Lupus nephritis
- Post streptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN)
Examination
On Admission:
Appearance
- Awake and alert, periorbital oedema, bilateral oedema of the hands and feet and mild tachypnoea at rest.
Vitals
- Temperature: 37C, afebrile
- BP:160/100 mmHg, hypertensive
- HR:85 beats per minute, tachycardic
- RR:20 breaths per minute, tachypnoei
General
- Mild conjunctival pallor
- Peri orbital oedema and bilateral oedema of the hands and feet
Cardiovascular
- Tachycardia
- Hypertensive
- JVP elevated to the angle of the jaw
Respiratory system
- Mild tachypnoea
- Bilateral basal crackles
Abdomen
- Not distended
- No tenderness
- No organomegaly
- Bowel sounds present
CNS
- Normal level of consciousness, alert and co-operative
- Gait, power, tone, sensation and reflexes intact and functioning within normal limits.
Dermatological
Mild scarring from healed lesions noted on thighs.
| Investigations | Results | Reference ranges |
|---|---|---|
| WCC | 5.31 | 4-12×10 9 /L |
| HB | 11.5 | 12.1-15.2g/L |
| Platelets | 219 | 140-450×10 9 /L |
| Normocytic normochromic anaemia | ||
| Urea | 38 | (2.5-6.4 mmol/L) |
| Creatinine | 780 | (50-80 umol/L) |
| K | 6.1 | (3.3-5.0 mmol/L) |
| Inorganic phosphate | 4 | (0.8-1.4 mmol/l) |
| Calcium | 1.9 | (2.1-2.6 mmol/l) |
| Complement | ||
| CH50 | Low | |
| C3 | Low | |
| C4 | Normal | |
| ASOT | 1280 | (>200 significant) |
| Anti-DNAse B | Positive to a titre of 360 | (>800 significant) |
| Blood Gas | ||
| pH | 7.2 | (7.38-7.42) |
| pCO2 | 3.8 | (4.5-6.1 kPa) |
| Base excess | -17 | (-2 to +2) |
| Bicarbonate | 12 | (22-30 mmol/l) |
| Anion gap | 22 | (10-15) |
| Urine Dipstix | ||
| Blood | 4+ | Negative |
| Protein | 2+ | Negative |
| Dysmorphic red cells | Present |
Urine:
- Oliguric, showing blood and protein on examination (see results table)
Chest X ray:
- Fluid overload
ECG
- Normal
Further clinical course:
- The patient persisted with rapidly progressive renal failure, a glomerular filtration rate failing to normalize, persistent hypocomplementemia, haematuria and proteinuria.
A renal biopsy was ordered, with the following findings:
Light microscopy
- Hypercellularity of the glomeruli with enlarged glomerular tufts
- Neutrophils and monocytes
- Crescent formation noted in 30% of the glomeruli
Immunofluorescence
- Deposits of immunoglobulin G and C3 present along the glomerular capillary wall and mesangium.
Electron microscopy
- Occasional patchy thickening in the glomerular basement membrane
- Humps of electron-dense immune-type deposits noted in the glomerular basement membrane overlying the mesangium.
Consistent with poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN)
Discussion
Background
The most common form of acute glomerulonephritis is a diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis that follows infections caused by group A beta-haemolytic streptococci. A classic case follows a streptococcal infection by 7-12 days. This is the time needed for the development of antibodies. Our case study focuses on this disease progression and series of graphics explains how the inflammatory response is caused by an immune reaction following the entrapment of immune complexes in the glomerular capillary membrane. The resulting proliferation of the glomerular capillary endothelial cells and the mesangial cells causing swelling of the capillary membrane and the accompanying signs and symptoms of post streptococcal glomerulonephiritis.
Before we discuss the immune response in relation to disease progression we will first look at the pathology involved in this disease and the healthy functioning kidney.
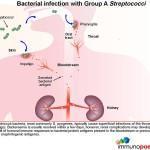
Bacterial infection with Group A Streptococci
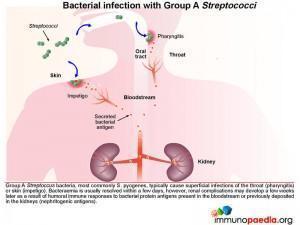 Group A Streptoccus bacteria, most commonly S. pyogenes, typically cause superficial infections of the throat (pharyngitis) or skin (impetigo). Bacteraemia is usually resolved within a few days, however, renal complications may develop a week or two later as a result of the humoral immune response to blood borne bacterial proteins that have specifically become deposited or “planted” in the kidneys (nephritogenic antigens). These nephritogenic antigens are thought to mediate damage to the glomerular basement membrane which disrupts the filtering function and allows antigens to cross into the Bowman’s space.
Group A Streptoccus bacteria, most commonly S. pyogenes, typically cause superficial infections of the throat (pharyngitis) or skin (impetigo). Bacteraemia is usually resolved within a few days, however, renal complications may develop a week or two later as a result of the humoral immune response to blood borne bacterial proteins that have specifically become deposited or “planted” in the kidneys (nephritogenic antigens). These nephritogenic antigens are thought to mediate damage to the glomerular basement membrane which disrupts the filtering function and allows antigens to cross into the Bowman’s space.
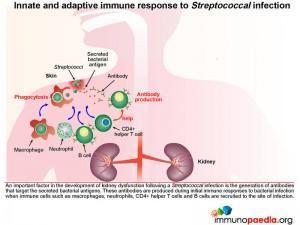 The innate and adaptive immune response to Streptococcal infection
The innate and adaptive immune response to Streptococcal infection
Innate immune cells such as macrophages and neutrophils migrate to sites of infection and help to destroy bacteria. The adaptive immune system is also activated with the recruitment of CD4+ helper T cells and B lymphocytes responding to bacterial antigens. An important factor in the development of kidney dysfunction following a Streptococcal infection is the generation of antibodies that target the secreted bacterial antigens.
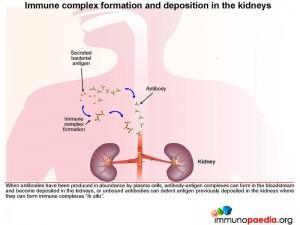 Immune complex formation and deposition in the kidneys
Immune complex formation and deposition in the kidneys
There are two possible explanations of how immune complexes become deposited in the kidney.
As plasma cells produce more and more antibodies, antibody-antigen complexes can form in the bloodstream due to the presence of secreted antigens and antibodies. These immune complexes can then become deposited in the kidneys via the circulation. Alternatively antibodies bind to free antigen already trapped in the glomerular basement membrane to form “in situ” immune complexes during glomerular filtration due to disrupted barrier function between the capillaries and the Bowman’s capsule.
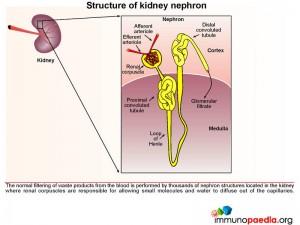
To better understand the complications caused by immune complex deposition in the kidneys we will briefly look at the structure and functioning of a healthy kidney.
The normal filtering of waste products from the blood is performed by thousands of nephrons located in the kidney. These are composed of several structures including renal corpuscles, responsible for filtering large amounts of fluid from the blood.
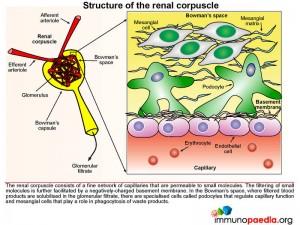 Structure of the renal corpuscle
Structure of the renal corpuscle
The renal corpuscle consists of two main parts: the glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule. The glomerulus is a fine network of capillaries that are permeable to small molecules. The glomerular capillary membrane is similar to that of other capillaries except that it has three major layers instead of the usual two. The (1) endothelium, (2) basement membrane and (3) layer of epithelial cells (continuous with the epithelium lining the Bowman’s capsule) known as podocytes, that surround the outer surface of the capillary basement membrane. Podocytes have long processes (foot processes) that wrap themselves around the glomerular capillaries. Each component brings its own unique function- the endothelium is fenestrated, the basement membrane has a negative electrical charge and prevents the passage of plasma proteins and the podocyte foot processes form slit-pores – that together form a highly efficient filtration system. Fluid from the glomerular capillaries leaks out across these layers into Bowman’s capsule that surrounds the glomerulus. This glomerular filtrate contains only water and small molecules. Another important component of the renal corpuscle is the mesangium. This occurs in areas where the capillary endothelium and basement membrane do not completely surround each capillary. The mesangial cells instead provide support in these areas by producing an intercellular substance similar to that of the basement membrane. They also possess phagocytic properties and remove materials that enter the intercapillary spaces. Typically this area is narrow and contains only a small number of cells, however mesangial hyperplasia and increased mesangial matrix occur in a number of glomerular diseases.
Now that we have an understanding of the anatomy of the renal corpuscle we can look more closely at how streptococcal antigen is deposited in the kidney.
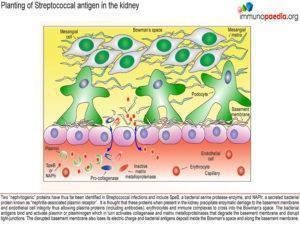 Planting of Streptococcal antigen in the kidney
Planting of Streptococcal antigen in the kidney
Two “nephritogenic” proteins have thus far been identified in Streptococcal infections and include SpeB, a bacterial serine protease enzyme, and NAPIr, a secreted bacterial protein known as “nephritis-associated plasmin receptor”. It is thought that these proteins when present in the kidney precipitate enzymatic damage to the basement membrane and endothelial cell integrity, thus allowing plasma proteins, erythrocytes and immune complexes to cross into the bowman’s space i.e. the system becomes “leaky”. The bacterial antigens bind and activate plasmin or plasminogen which in turn activates the enzymes collagenase and matrix metalloproteinases that degrade the basement membrane and weaken endothelial cell tight-junctions. Disrupted membrane function allows bacterial antigens to be deposited inside the Bowman’s space
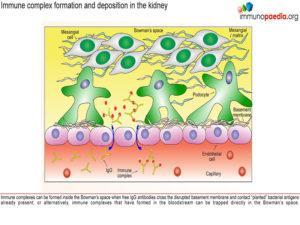 Immune complex formation and deposition in the kidney
Immune complex formation and deposition in the kidney
Immune complexes can be formed inside the Bowman’s space when free IgG antibodies cross the disrupted basement membrane and contact “planted” bacterial antigens already present, or alternatively, immune complexes that have formed in the bloodstream can also cross the weakened barrier and become trapped in the Bowman’s space.
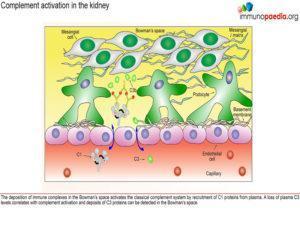 Complement activation in the kidney
Complement activation in the kidney
The deposition of immune complexes in the Bowman’s space activates the classical complement system by recruitment of C1 proteins from plasma. A loss of plasma C3 levels (see investigations) correlates with complement activation and deposits of C3 proteins can be detected along the basement membrane and in the Bowman’s space.
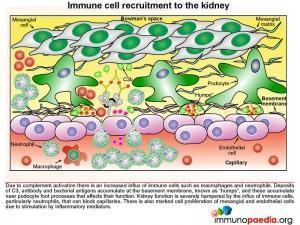 Immune cell recruitment to the kidney
Immune cell recruitment to the kidney
Due to complement activation and generation of anaphylatoxins we then see an increased influx of immune cells such as macrophages and neutrophils. Deposits of C3, antibody and bacterial antigens accumulate at the basement membrane near the podocyte foot processes, known as “humps”. Kidney function is severely hampered by influx of immune cells, particularly neutrophils, that can block capillaries. There is also marked cell proliferation of mesangial and endothelial cells due to the presence of soluble inflammatory molecules.
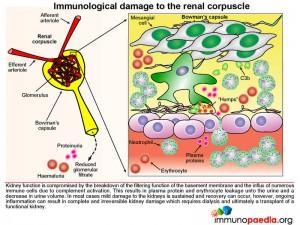 Immunological damage to the renal corpuscle
Immunological damage to the renal corpuscle
Kidney function is compromised by the breakdown of the filtering function of the basement membrane and the influx of numerous immune cells due to complement activation. This results in plasma protein (proteinuria) and erythrocyte (haematuria) leakage unto the urine and a decrease in urine volume (oliguria). Oliguria which develops as the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) decreases is one of the first symptoms. Proteinuria and haematuria follow because of increased glomerular capillary wall permeability. The red blood cells are degraded and cola coloured urine is one of the early signs of the disorder. Sodium and water retention gives rise to oedema, particularly in the face and hands and the patient is also found to have hypertension due to salt imbalance. Laboratory findings include elevated antistreptolysin O titre (antibodies to a streptococcal exoenzyme) a decline in C3 complement and cryoglobulins. In most cases only mild damage to the kidneys is sustained and the patient will recover, but ongoing inflammation can result in complete and irreversible kidney damage that requires chronic dialysis and ultimately a transplant of a functional kidney.
Download images for this case
Treatment
Symptomatic therapy is recommended for patients with acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis, and it should be based on the clinical severity of the illness. The major goal is to control fluid balance and blood pressure.
This patient did not respond to diuretics, remaining fluid overloaded with pulmonary oedema and persistent oliguria. The patient required urgent dialysis, which was continued for three weeks.
Download images for this case
Final Outcome
The patient did not recover from her three weeks of dialysis.
She was then assessed for the chronic dialysis program and work up was started for the transplant program.
Download images for this case
References
Kambham N. (2012) Postinfectious glomerulonephritis. Adv Anat Pathol. Sep;19(5):338-47.
Oda T et al (2012). The role of nephritis-associated plasmin receptor (NAPlr) in glomerulonephritis associated with streptococcal infection. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012:417675.
Rodríguez-Iturbe B, Batsford S (2007) Pathogenesis of poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis a century after Clemens von Pirquet. Kidney Int. Jun;71(11):1094-104.
Wong W, Morris MC, Zwi J. (2009) Outcome of severe acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis in New Zealand children. Pediatr Nephrol. May 2009;24(5):1021-6.
Download images for this case
Evaluation – Questions & answers
What was the final diagnosis?
What is an important factor in the development of kidney dysfunction following a streptococcal infection?
What are the three layers that make up the filtration membrane of the glomerulus?
How are the two nephritogenic proteins SpeB and NAPIr thought to contribute to PSGN?
How does the basement membrane become degraded?
Download images for this case
Multiple Choice Questions
Earn 1 HPCSA or 0.25 SACNASP CPD Points – Online Quiz
Download images for this case